Analyzing Data in Heat Maps
In this section you will learn how to:
•Create a gate on a heat map
•Use well gates to view events in 2D plots from single and multiple wells
•Create heat map overlays to view events from multiple wells on a single plot as an overlay
We will be using a data set that is looking for wells (hits) that are positive in the FL2-A channel. We will be using the HighContentAnalysis.fey layout and the HighContent96wellData.dns data file (.dns is special file format created by FCS Express), which are both located in the Tutorial Sample Data archive. The original data set contains 96 FCS Files acquired on a plate-based acquisition system.
1.Load the HighContentAnalysis.fey layout.
2.Choose the Data tab→Organize Data Sets→Data List command (Figure T9.2).
3.Click the ![]() symbol to Add Data Files to the data list.
symbol to Add Data Files to the data list.
4.Choose DNS data Stream files (*.dns) from the Files of type: drop-down list (Figure T18.17).
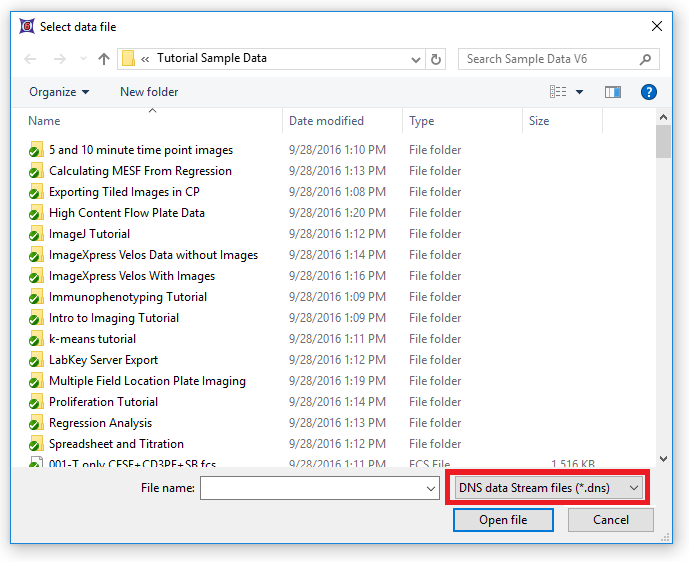
Figure T18.17 Choosing DNS Data Stream Files
5.Navigate to the FCS Express Tutorial Sample Data directory (Figure T18.18).
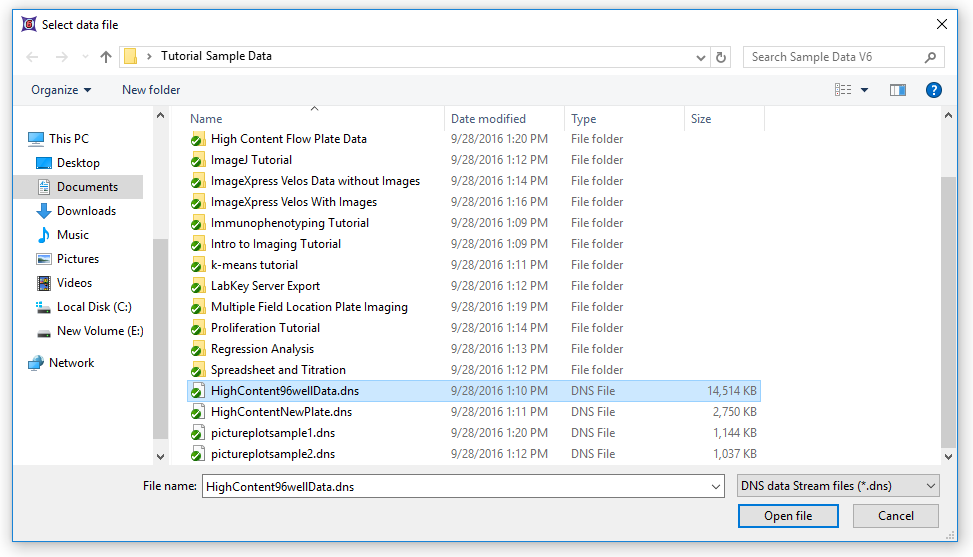
Figure T18.18 Choosing the HighContent96wellData.dns file
6.Choose the file "HighContent96wellData.dns"
7.Click Open file (Figure T18.18, above).
The file will now appear in the data list as a file. This file contains data from all 96 wells stored in .dns format. We will now load the data into the plots on the layout before we insert a heat map.
8. Choose the Data tab→Change Data on All→Select→Select using Advanced Open Data Dialog command (Figure T18.18a).
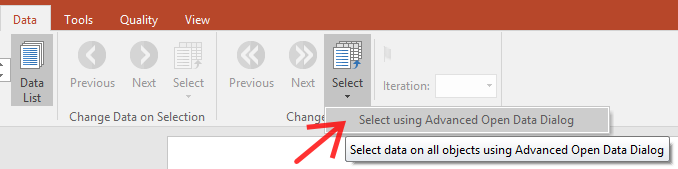
Figure T18.18a. Select Using Advanced Open Data Dialog command.
9. Choose the Data List tab in the resulting Change Data File dialog.
10. Highlight the HighContent96wellData.dns file and click OK.
Note: Alternatively you can select the "HighContent96wellData.dns" item in the Data List and click on "Change Data On All Plots" (Figure T18.18b)
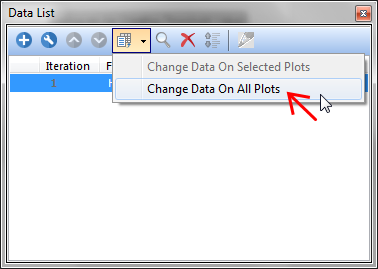
Figure T18.18b - Change Data On All Plots button
11.The layout will now look like Figure T18.19.
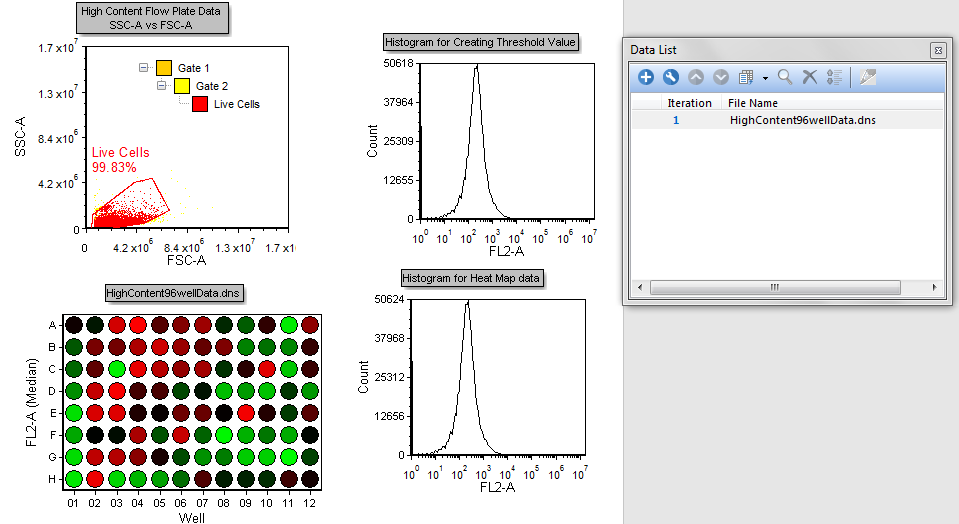
Figure T18.19 High Content Analysis Layout after Loading HighContent96wellData.dns File
The color dot plot in the layout is showing all the events within the .dns file (Figure T18.19). The Live Cells gate is applied to the heat map so it will only display cells falling within the gate, defined on the 2D plot.
Wells that are "hot" for FL2-A are displayed in red and wells that are "cool" for FL2-A are displayed in green. Varying degrees of heat are represented by the transition from Red to Black to Green.
We will now create gates into the heat map.
12. Right-click on the Heat Map.
13. Choose Create Gate→Well from the pop-up menu.
14. Click in the white space surrounding the plate but within the green selection as in Figure T18.20 (clicking directly on a well will immediately select the well for gating).
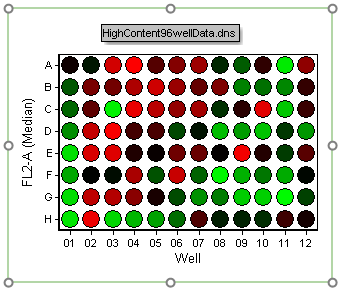
Figure T18.20 Creating a Well Gate
The Editing New Well Gate window will appear (Figure T18.21).
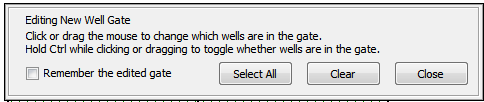
Figure T18.21 Editing a New Well Gate
15. Click on Well H12. The Create New Gate dialog will appear (Figure T18.21b).
16. Enter "Negative Control" for the gate name, change the gate color to "Green" and click OK (Figure T18.21b).
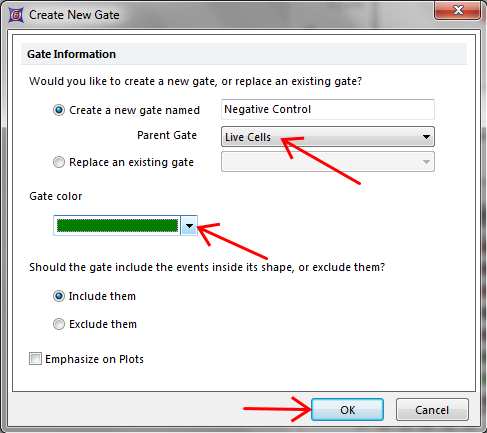
Figure T18.21b - Create New Gate window
We will now create a second gate into the heat map called "Experimental". For training purpose we will use an alternative procedure to steps 12-16.
17. Choose the Gating→Create Gates→Well command (Figure T18.22).
Figure T18.22 Selecting the Create Well Gate Command
18. Click directly on Well A4. The Create New Gate dialog will appear (similar to Figure T18.21b).
19. Enter "Experimental" for the gate name, change the gate color to Blue and click OK.
The layout and gate view should now look like Figure T18.23.
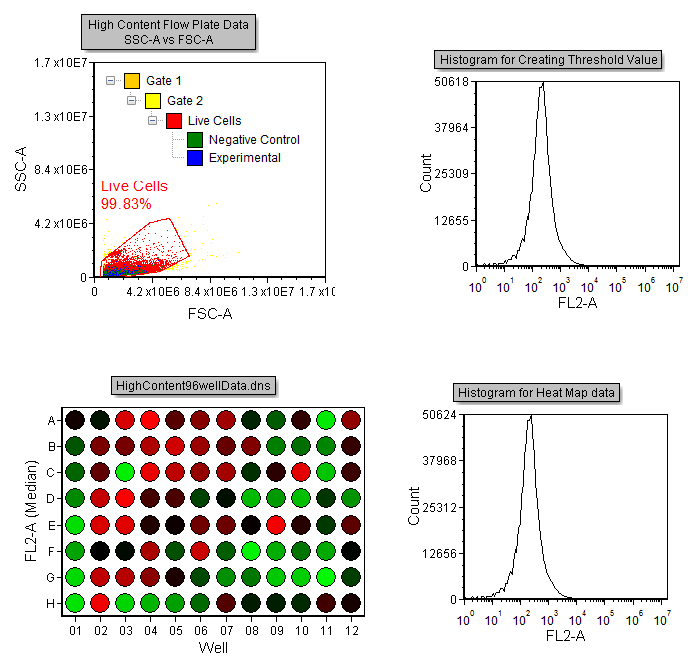
Figure T18.23 Layout with Gate View Indicating Hierarchical Gating of the Negative Control and Experimental Gates
We will now create a histogram overlay to view data from separate wells.
20. Drag and drop the entire Heat Map to the plot labeled Histogram for Heat Map data on the layout (Figure T18.23b).
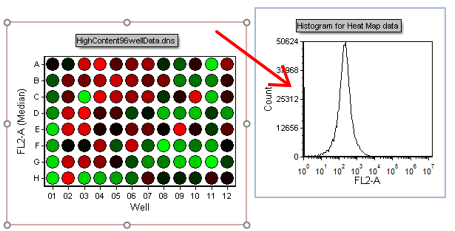
Figure T18.23b - Drag&Drop action to create overlay
21. The Select Drag and Drop Action window appears (Figure T18.23c)
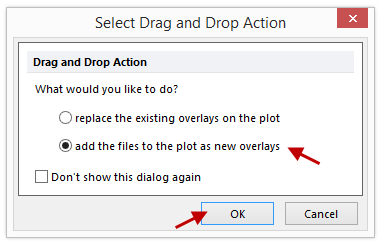
Figure T18.23c - Select Drag and Drop Action window
22.Select the option to Add the files to the plot as new overlays and click OK (Figure T18.23c).
23. Right-click on the histogram.
24. Choose Format from the pop-up menu and select the Overlays category.
Two overlays for the same FCS Plate folder file will be displayed in the Overlay list.
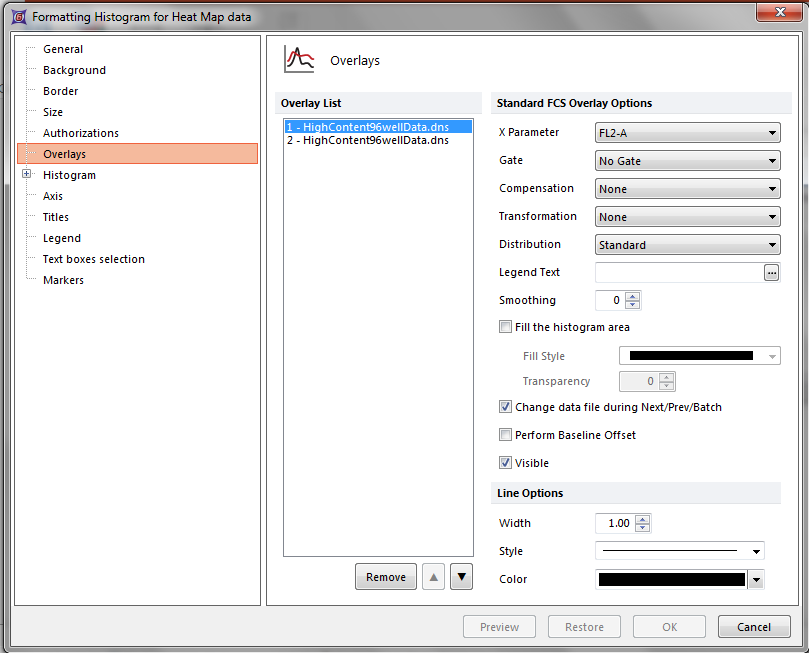
Figure T18.23d - Formatting Histogram for Heat Map data windows
25.Highlight the first overlay in the Overlay List.
26.Change the Gate to "Negative Control".
27.Change the Color under Line Options to Green.
28.Highlight the second overlay in the list.
29.Change the Gate to "Experimental".
29.Change the Color under Line Options to Blue.
30.Click OK.
The Histogram will now look like Figure T18.24, displaying the cells in the "Negative Control" well gate as green, and the cells from the "Experimental" well gate as blue.
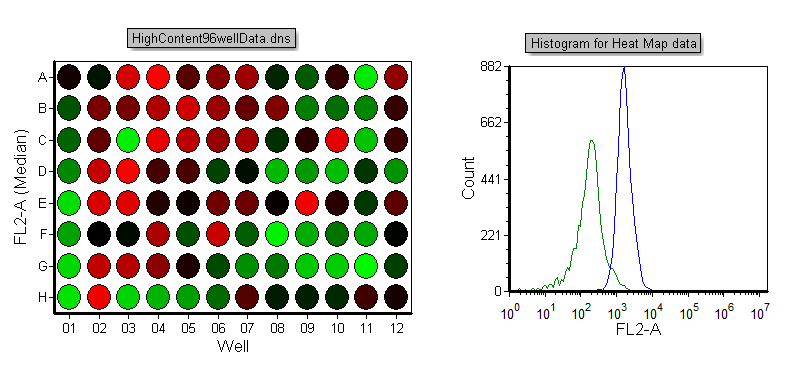
Figure T18.24 Histogram Displaying Events from Well Gates
We will now edit the well gates to select different wells.
31. Right-click on the Heat Map.
32. Choose Edit Gate→Experimental from the pop-up menu. The Editing well gates window will appear and well A4 will be highlighted in blue (Figure T18.25).
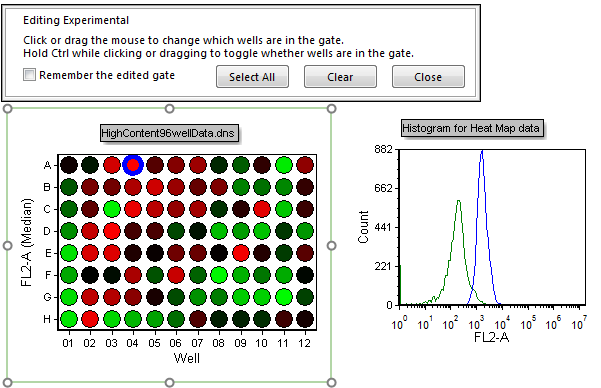
Figure T18.25 Editing the Experimental Well Gate (A4)
33. Click on well C12.
Notice how the experimental histogram peak shifts showing only the cells in the newly selected well (Figure T18.26).
Well C12 shows heterogeneous staining for FL-2A while "cooler" wells such as G9 (click on well G9 to view) overlap with the negative control. We will now select multiple "Negative" wells to create a better picture of the negative population on the histogram.
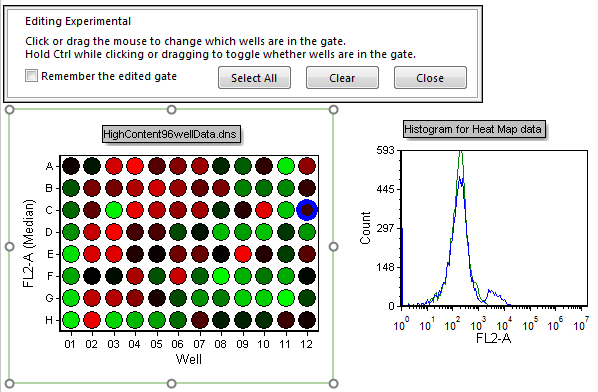
Figure T18.26 Experimental Well Gate Changed to C12
34. Hit Ctrl+Z to undo the gate change.
35. Right-click on the Heat Map.
36. Choose Edit Gate→Negative Control from the pop-up menu.
37. Press and hold down the Ctrl button to allow multiple non-consecutive selection.
38. Click on wells C1 and F1 (Figure T18.27).
39. Release the Ctrl button.
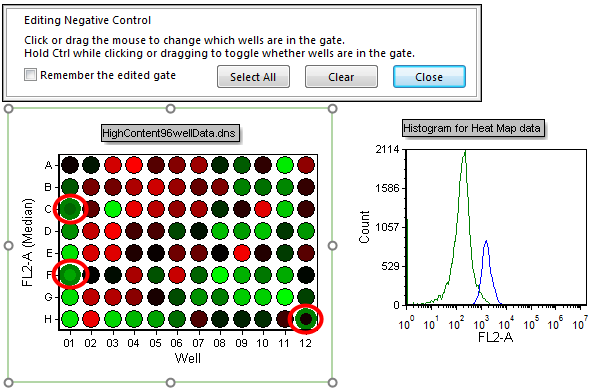
Figure T18.27 Selecting Multiple Non-consecutive Wells (C1, F1, and H12)
Multiple non-consecutive wells can be chosen in this manner. Notice how the histogram updates to reflect selection of the multiple wells (C1, F1, and H12 in Figure T18.27). We will now select multiple wells using a selection box.
40. Left-click and hold the mouse button down just above and to the right of well B1.
41. Drag the mouse down and to the left to select wells B1-F1. Notice how the selection box appears and indicates which wells are being selected (Figure T18.28).
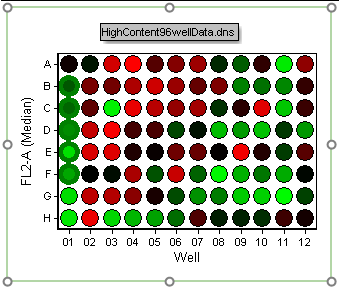
Figure T18.28 Selecting Multiple Continuous Wells
42. Release the mouse button to select the wells.
Multiple wells can also be selected by a combination of using the selection box and Ctrl+Clicking.
43. Hold down the Ctrl key.
44. Select wells B1-F1.
45. Click on well G9 to select it (continue holding down the Ctrl key).
46. Create a new selection box (with the Ctrl key still being held down) to encompass wells A8-A11.
47. Release the Ctrl key.
48. Click Close from the Editing Well Gate window.
Wells B1-F1, A8-A11, and G9 are now selected and contributing to the Negative Control histogram peak (Figure T18.29).
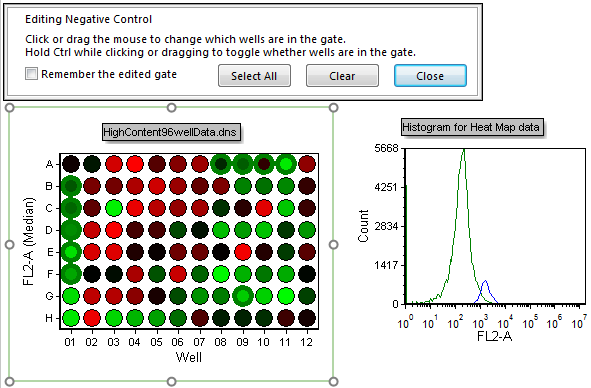
Figure T18.29 Multiple Well Selection
Gates may also be deselected from the well gating dialog in a similar manner.
49. Right-click on the Heat Map.
50. Choose Edit Gate→Negative Control from the pop-up menu.
51. Ctrl+Click on well A8. Notice how the well gate is removed.
52. Ctrl+Drag a selection box over wells B1-F1. The continuous column well gates will be removed.
Although selecting wells for gating and displaying them in histograms or 2D plots is useful, some users may be only interested in which wells contain the highest channel values. We will now format the heat map to display wells that are above a threshold value of interest.
53. Right-click on the Heat Map.
54. Choose Format from the pop-up menu.
55. Choose the Heat Map→Color Levels category.
56. Change the Style to Threshold from the drop down window (as in Figure T18.12).
57. Click on the ![]() symbol in the Threshold Value field to insert a token.
symbol in the Threshold Value field to insert a token.
58. Double-click on Statistic from the Insert a Token dialog.
59. Choose the "Histogram for Creating Threshold Value" in the Select a plot list box.
60. Choose the Statistic category on the left of the Create Statistic dialog.
61. Set the Gate to Live Cells from the drop-down list.
62. Highlight Median in the Statistic list box.
63. Click OK.
64. Change the Below Threshold Color to Black, Above Threshold Color to Red and click OK.
The heat map will now look like Figure T18.30. The red wells indicate which wells have median FL2-A fluorescence that are above the median FL2-A fluorescence of the entire plate.
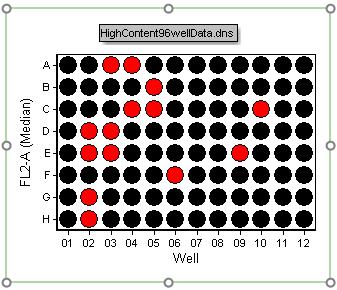
Figure T18.30 Threshold Defined as Median Value
In the next section, we will use batch analysis to analyze multiple plates.
