Automatic Compensation - Optional Step 4
Please note this tutorial section is for Optional Step 4 associated with compensation and is designed with more advanced FCS Express users in mind.
Once you have completed Step 1 of the Automatic Compensation Setup, you can go through Optional Steps 4 and/or 5 (see next chapter for more details on Step 5). This tutorial will walk you through a sample compensation setup using Step 4. If you are not yet familiar with automatic compensation in FCS Express, please complete the Automatic Compensation tutorial before starting this section.
Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) allows you to define your single-stained controls on gates other than the default markers created during the automatic compensation setup.This step is useful when you would like to refine the populations that are used for calculating compensation. For instance, if the Automatic Compensation Setup does not make a good estimate of the population, or if you would like to use a population from another file, gate, gating hierarchy, or plot Step 4 would prove very useful. Parameters may be adjusted or changed all together by dragging and dropping a plot or gate onto the parameter for the Stained and Unstained columns. If a gate is dropped the compensation definition will be based on that gate and plot it originated from (keep in mind any gating hierarchy you have defined with a gate will be used) . If a plot is dropped, the compensation definition will be based on the plot that you just dropped, with the gating being unchanged. Dragging and dropping new plots, files, or gates in this section will allow you to override the automatic setup and use gates and plots of your choice.
The layout that will be used for this section of the tutorial is AutoCompAdditionalSteps.fey and it can be found in the Tutorial Sample Data archive. In this layout, an automatic compensation setup definition (named New Automatic Compensation) has already been created using the standard default setup described in the previous section. The layout contains 6 pages as follows:
•Gating Strategy and Sample page: The Gate View on this page shows the gating strategy that was created automatically by the compensation setup (purple gates) and the one that we would like to use (red and blue gates). The plots are arranged starting from the top left to show how the gating hierarchy has been applied. Follow the green arrows next to each plot to see how the gates have been applied and defined. The plot labeled SAMPLE COMPENSATION has the New Automatic Compensation definition applied to it. The plot off the page to the right is labeled Data for New Compensation Gates and has no compensation applied to it. The Data for New Compensation Gates plot has gates drawn on the PE positive, PerCPCy5-5 positive, and negative populations. These gates will be used later in the tutorial for the adjust parameters steps.
•Spillover Spreading Matrix page: This page was created automatically by the Automatic Compensation Setup tool and displays fluorescence signal interactions.
•Cross Stain Index Matrix page: This page was created automatically by the Automatic Compensation Setup tool and quantifies the spread of a given dye into another dye.
•Scatter Plot page: This page was created by the Automatic Compensation Setup tool and displays the stained and unstained populations used to calculate the compensation matrix.
•CD 62L page: This page was created by the Automatic Compensation Setup tool and displays the current gate used to calculate the compensation matrix for the PE parameter.
•CD 4 page: This page was created by the Automatic Compensation Setup tool and displays the stained and unstained populations used to calculate the compensation matrix for the PerCPCy5-5 parameter.
In the following steps, we will adjust the parameters to define new gates for the single stained and unstained controls.
1. Select File tab→Open (Figure T3.1).
2. Open the layout AutoCompAdditionalSteps.fey found in the Tutorial Sample Data archive.
3.Click Tools tab→Transformations group→Compensation and Unmixing command to open the Compensation and Unmixing navigator.
4.Expand the Create Manually folder, then select the New Automatic Compensation.
5.Select the Automatic Compensation Setup tab.
6. Click on Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) (Figure T8.22).
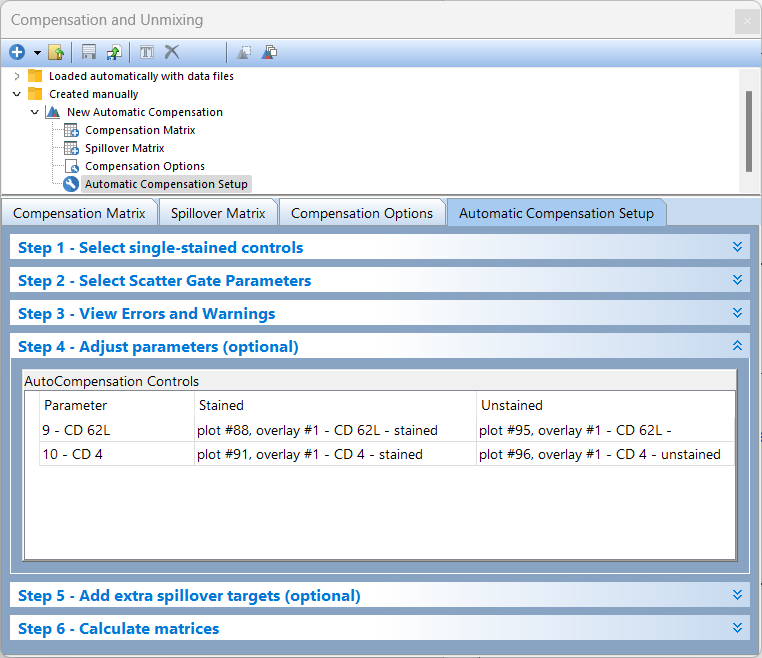
Figure T8.22 Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) of Automatic Compensation Setup
We now will replace the gates that were defined in the Automatic Compensation Setup with gates we have defined manually. These manually defined gates represent the following:
•A gating hierarchy has been defined with all of the FSC and SSC parameters and a Dapi Negative gate. This hierarchy is used to exclude debris and other unwanted events.
oNegative Control Gate: This gate is a child of the Dapi Negative Gate hierarchy. It defines a negative or unstained control population.
oPE Positive Control gate: This gate is a child of the Dapi Negative Gate hierarchy. It defines a PE single color control only population.
oPerCP CY5-5 Positive Control gate: This gate is a child of the Dapi Negative Gate hierarchy. It defines a PerCP CY5-5 single color only population.
7. Click and hold on the Negative Control gate in the gate view (Figure T8.23).
8. Drag and drop the Negative Control gate onto the cell for Unstained column in the CD62L YG PE-A row.
9. Click and hold on the Negative Control gate in the gate view.
10. Drag and drop the Negative Control gate onto the cell for the Unstained column in the CD4 PerCP-Cy5-5-A row.
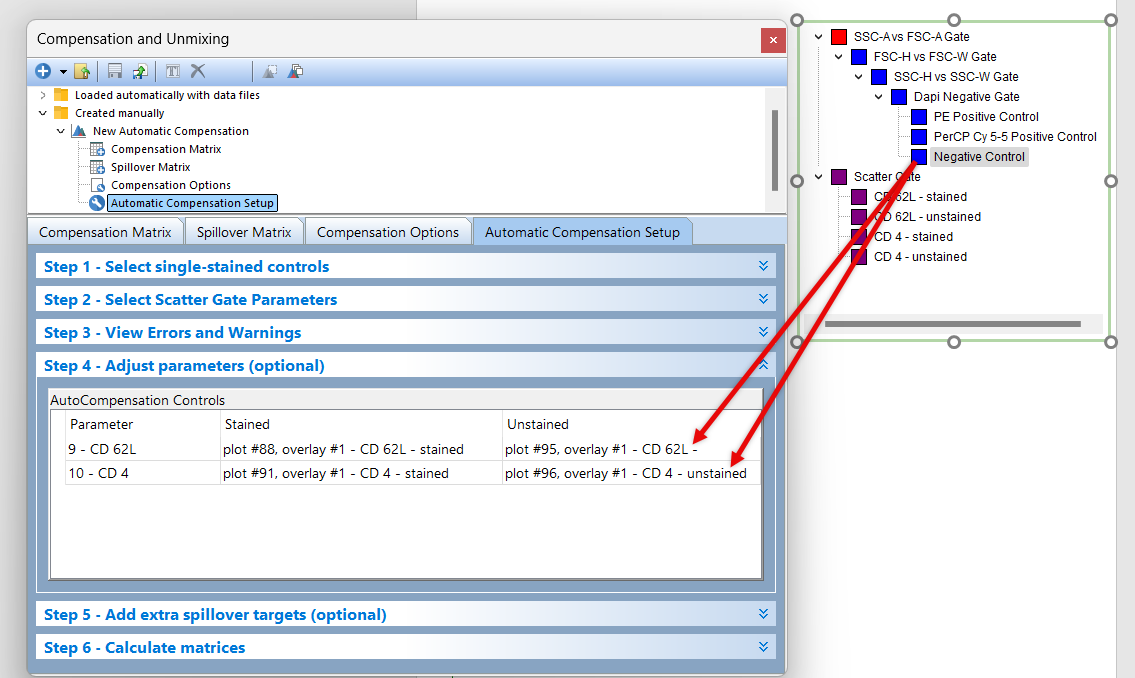
Figure T8.23 Dragging the Negative Control gate from the gate view to the Unstained column for both parameters.
Now, the Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) section should resemble Figure T8.24, lower panel.
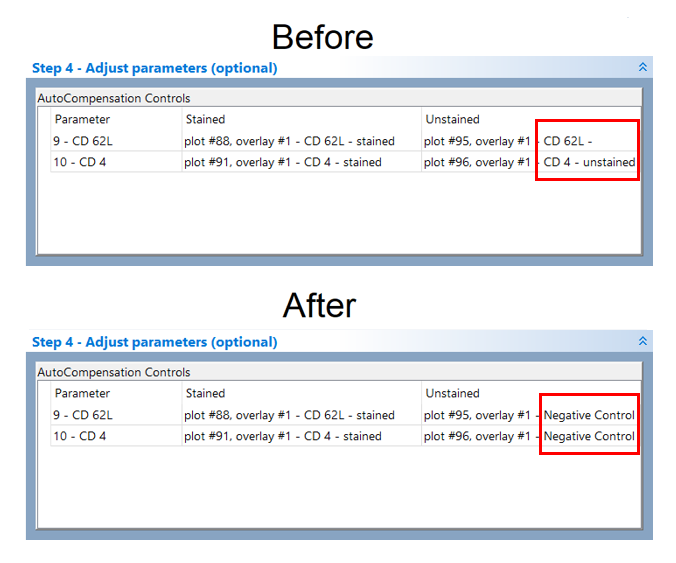
Figure T8.24 Paramters in Step 4 section before and after the drag and drop
In the steps above we dragged and dropped the Negative Control gate from the Gate View. We will now use a plot as source for the drag and drop (Figure T8.25).
11. Click and hold on the PE Positive Control gate in the Data for New Compensation Gates plot (off the right hand side of page).
12. Drag and drop it onto the cell for the Stained column in the CD62L YG PE-A row.
13. Click and hold on the PerCPCY5-5 Positive Control gate in the Data for New Compensation Gates plot (off the right hand side of page) (Figure T8.25).
14. Drag and drop it onto the cell for the Stained column in the CD4 PerCP-Cy5-5-A row.
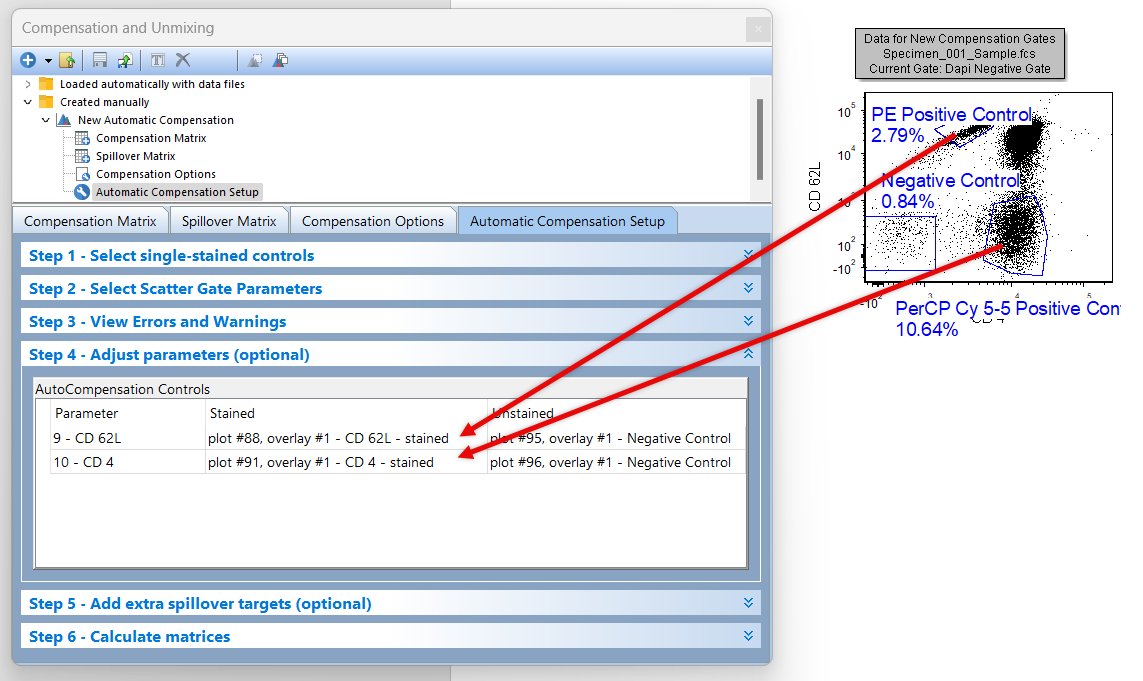
Figure T8.25 - Dragging and dropping gates from a plot to the Stained column in step 3 for each parameter.
Now, the Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) section should resemble in Figure T8.26, lower panel.
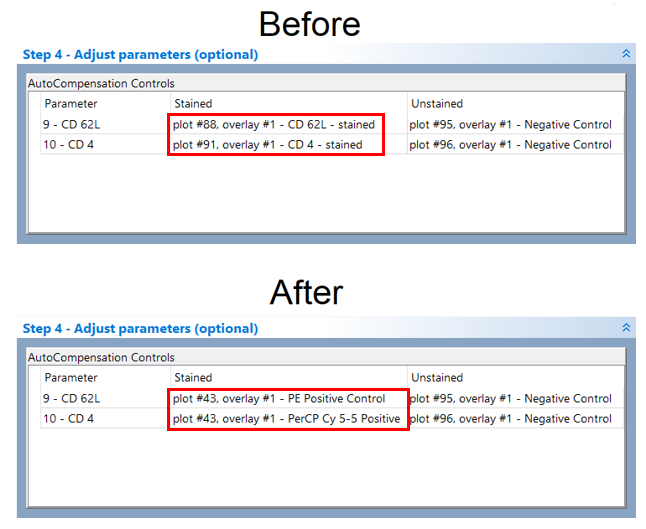
Figure T8.26 Step 4 - Adjust parameters (optional) after dragging and dropping gates from the Gate View and plot to define the stained and unstained population columns.
15. The Spillover matrix and Compensation Matrix will automatically be updated after making these changes.
Notice the spillover matrix for the New Automatic Compensation definition has changed (see Figure T8.27 below) to reflect the new gating changes. You can drag and drop any gate or an entire plot to the Stained and Unstained columns in this fashion to customize your Automatic Compensation Setup.
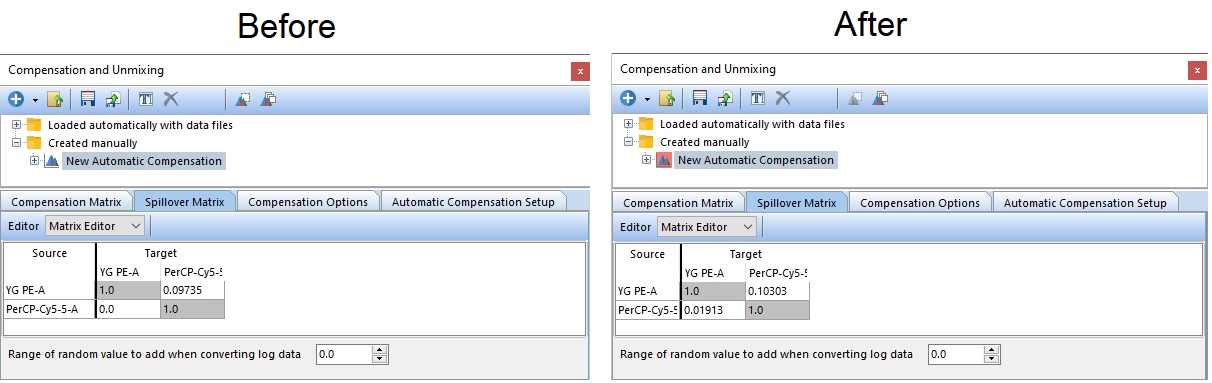
Figure T8.27 The original Automatic Compensation Setup definition (left) compared to one generated using gates manually defined gating hierarchy from the steps above.
TIP: A useful trick to refine the populations used to calculate the compensation matrix (e.g. toe xclude debris), is to rearrange the gate hierarchy. For example, in the layout above, the Scatter Gate and its children (i.e. the gates defined by the Automatic Compensation Setup) could be moved into a different place in the gate hierarchy so that they become children of another gate that you have created.
This brings us to the end of the tutorial for Automatic Compensation Optional Step 4.
If you would like to learn about Step 5-Add extra spillover targets (optional), proceed to the tutorial on Automatic Compensation Optional Step 5.
