2D Plot Statistics
There are two kinds of statistics that can be displayed for a 2D plot (Gate Statistics and Quadrant Statistics). The same statistics are available in either case.
| • | Gate Statistics |
The statistics are calculated for every gate designated in the Gates to Display data option for the statistics window, even if the gate is not being displayed on the plot. The Gates to Display can be chosen from a dialog accessible from the Format→Data Options→Gates To Display command, or in the Formatting Statistics dialog shown by right-clicking on the statistics window and choosing Format from the pop-up menu.
| • | Quadrant Statistics |
The statistics are calculated for every quadrant. There will be four rows of statistics for each overlay with each row corresponding to a different quadrant. Quadrant statistics displayed on the plot may be changed by formatting the Label Text Box containing the statistic.
In order to open a statistics window, right-click on a 2D Plot and choose Gate Statistics (Figure 9.26, ![]() ) or Quadrant Statistics (if quadrants are not currently shown on the plot, this option is not enabled) from the pop-up menu. Individual statistics may be toggled on and off by right-clicking on the default statistics table (Figure 9 below,
) or Quadrant Statistics (if quadrants are not currently shown on the plot, this option is not enabled) from the pop-up menu. Individual statistics may be toggled on and off by right-clicking on the default statistics table (Figure 9 below, ![]() ), or from the Formatting Statistics menu.
), or from the Formatting Statistics menu.
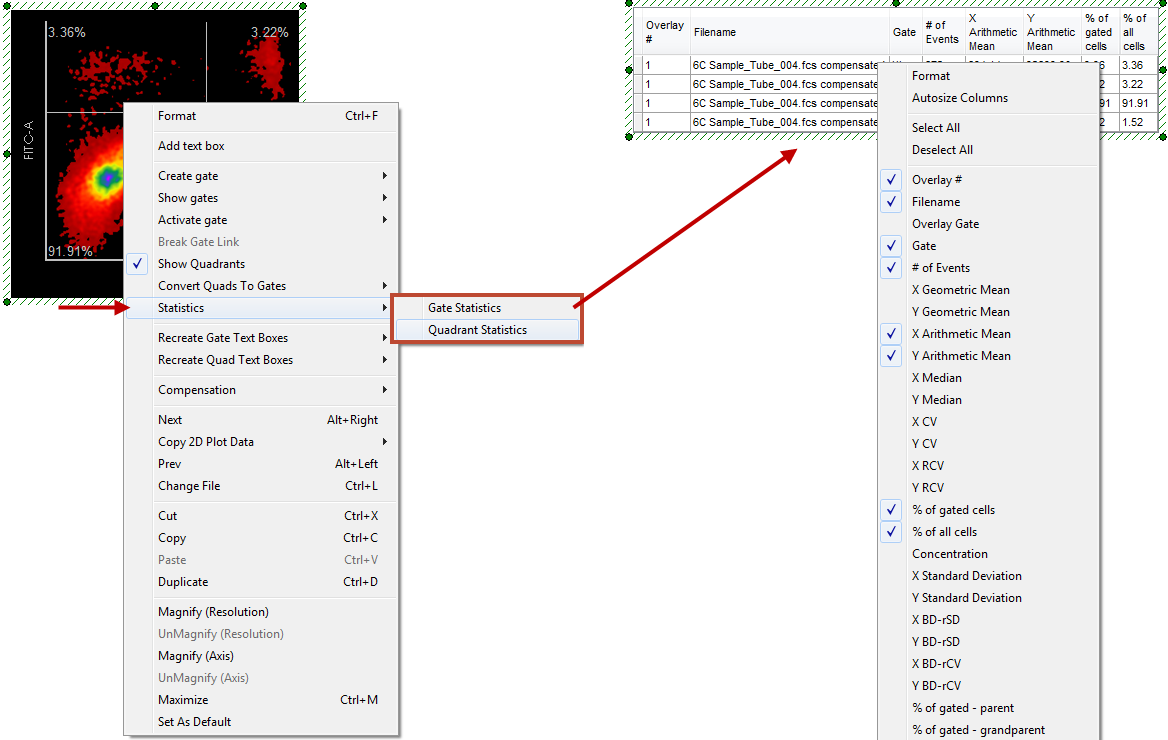
Figure 9.26 Adding a default statistics table from a 2D plot
The available statistics are shown in the table below. A region can refer to a gate or quadrant.
Statistic |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Overlay # |
If there are multiple overlays visible on a plot, the statistics will be calculated for every overlay on the plot. Overlay # displays the overlay number for that row of statistics. The overlay number corresponds to the position in the overlay list on the Overlays page of the Format window. |
FCS Filename |
The file name corresponding to the overlay number. |
Overlay Gate |
The name of the gate that is currently being applied to the overlay. |
Gate |
The region for which the statistics apply. This region can be either a gate or quadrant designation. |
# of Events |
The total number of events in this region accepted by the gating formula. |
X Geometric Mean |
The geometric mean channel number of the events on the X-axis that are accepted by the gating formula. Similar to arithmetic mean except that the numbers are multiplied and the Nth root of the resulting product is taken. |
Y Geometric Mean |
The geometric mean channel number of the events on the Y-axis that are accepted by the gating formula. Similar to arithmetic mean except that the numbers are multiplied and the Nth root of the resulting product is taken. |
X Arithmetic Mean |
The mean X-axis channel value of cells in this region that are accepted by the gating formula. |
Y Arithmetic Mean |
The mean Y-axis channel value of cells in this region that are accepted by the gating formula. |
X Median |
The median X-axis channel value of cells in this region that are accepted by the gating formula. |
Y Median |
The median Y-axis channel value of cells in this region that are accepted by the gating formula. |
X CV (Coefficient of Variation) |
The coefficient of variation of X-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula that fall within the specified marker. The CV is a measure of the distribution of your data and is equal to the standard deviation divided by the mean. |
Y CV |
The coefficient of variation of Y-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula that fall within the specified marker. |
X RCV (Robust CV) |
The Robust Coefficient of Variation of X-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula. The RCV may be more applicable than the CV for populations that do not follow a normal Gaussian distribution. The RCV is equal to 0.75 multiplied by the interquartile range divided by the median. The interquartile range is the 75th percentile channel minus the 25th percentile channel. |
Y RCV |
The Robust Coefficient of Variation of Y-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula. |
% of Gated Cells |
The total events in the specified region divided by the total number of events on the whole plot accepted by the gating formula. |
% of All Cells |
The total events in the specified region divided by the total number of events in the FCS file. |
Concentration |
The concentration of the cells that are accepted by the gating formula. The parameters for the concentration calculation can be set up in the Concentration Calculator. |
X Standard Deviation |
A measure of the variation from the average for the events on the X-axis. The square root of the variance. |
Y Standard Deviation |
A measure of the variation from the average for the events on the Y-axis. The square root of the variance. |
X BD-rSD |
The BD Biosciences robust standard deviation for X axis events. See the full description by BD Biosciences. |
Y BD-rSD |
The BD Biosciences robust standard deviation for Y axis events. See the full description by BD Biosciences. |
X BD-rCV |
The BD Biosciences robust coefficient of variation of X-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula that fall within the specified marker. See the full description by BD Biosciences. |
Y BD-rCV |
The BD Biosciences robust coefficient of variation of Y-axis events that are accepted by the gating formula that fall within the specified marker. See the full description by BD Biosciences. |
% of Gated - Parent |
The number of events that are accepted by the gating formula and are inside the specified gate divided by the total number of events of the parent of the gate applied to a plot. |
% of Gated - Grandparent |
The number of events that are accepted by the gating formula and are inside the specified gate divided by the total number of events of the grandparent of the gate applied to a plot. |
