Exporting Plate Based Data That Contains Multiple Fields Per Well
Exporting Plate Based Data That Contains Multiple Fields Per Well
Often images of multiple fields within a single well of a plate format experiment are taken. CellProfiler can segment all of the individual field images and pool the data as a single well for export to FCS Express Image Cytometry. The resulting data sets may then be opened in FCS Express to review and analyze the data in Heat Maps, Picture Plots, Dot Plots, and Histograms.
In the course of this tutorial we will explain:
•Image naming conventions needed for FCS Express to import the multi well, multi field, imaging data processed by CellProfiler.
•Exporting Multiple Well, Multiple Field Location, Imaging data in CellProfiler for use in FCS Express.
Naming Conventions for Plate Based Multiple Field Location Image Data Sets
When reconstructing a series of plate based data containing multiple fields per well FCS Express will use information stored in the filename to assign well locations and to merge the multiple field images into a single image. In particular the regular expression names Row and Column (for well locations) and rowtile and coltile (for the field location within the well) should be used when exporting plate based data with multiple image locations per well. These names define the plate location of the well by Row Letter and Column Number and the location of the field within the well by rowtile and coltile position. To successfully use regular expression for processing the data in CellProfiler and analyzing the data in FCS Express the information for Well numbers and field locations must be stored somewhere within the filename of the image. In Figure T24.54 below the image name is: Channel1-01-A-01_00_00. The red box highlights the well Row and Column information (well A01), and the blue box highlights the field location (position 00, 00).
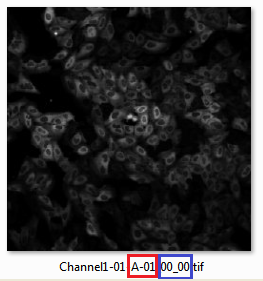
Figure T24.54 The image name is: Channel1-01-A-01_00_00. The red box highlights the well Row and Column information (well A01), and the blue box highlights the field location (position 00, 00).
Exporting Multiple Field Location Plate Imaging Data in CellProfiler for use in FCS Express
The CellProfiler modules that will be discussed in this section are Load Images, Save Images, and Export to Spreadsheet. The completed pipeline for this example can be found in the Tutorial Sample Data archive within the Multiple Field Location Plate Imaging folder is named MultipleFieldLocationPipelineCOMPLETED.cpproj. The completed pipeline is meant to be used as a template for comparison to your pipeline and represents the finished product of this tutorial.
The example data set we will be using can be found in the Tutorial Sample Data archive within the Multiple Field Location Plate Imaging folder. The example data set contains 16 images which are broken down into two channels of images (channel 1 and channel 2) and two wells (A1 and A2) with 4 fields per well.
The steps for exporting data from CellProfiler have been broken down by module according to the MultipleFieldLocationPipeline.cpproj pipeline. After loading the MultipleFieldLocationPipeline.cpproj pipeline in CellProfiler, follow the steps below to amend the pipeline to prepare for export to FCS Express.
Selecting Default Output Folder
To organize your data correctly for FCS Express, ensure the Default Output Folder is the same folder where your images are stored and used for the Default Input Folder (Figure T24.55 below).
Note: The DefaultOUT.mat file will also be exported to the Output Folder. This file is for use in MATLAB. If you do not wish to use this file, you can select Do not write MATLAB or HDF5 files from the Output file format drop-down menu.

Figure T24.55 Set the Default Input and Output Folders to the Same Location
A. Loading Images, Extracting Metadata, Assigning Names
In order for FCS Express to recognize your data is in 96 well format, metadata from the image file names must be extracted. A Regular Expression must be defined to find the metadata in the file name or path of the data by following these steps in CellProfiler (Figure T24.2):
1.Click Images category in left column of CellProfiler window.
2.Drag and drop Multiple Field Location Plate Imaging folder into designated area.
3.Click Apply filters to the file list to remove non-image files. Font for Experiment.ini should become gray.
4.Click Metadata category directly below Images.
5.Click Yes radio button in the Extact metadata? box.
6.Confirm Metadata extraction drop-down list is set to Extract from file/folders.
7.Confirm Metadata source drop-down list is set to File name.
8.Click the magnifying glass icon to the right of Regular Expression to field.
9.Erase all text from Regex: field.
10. Copy and paste following text into Regex: field, which will define the Channel Number, Well Number, Row of the plate with a letter, Column with a number, Row Tile with a number, and column tile with a number:
Channel1-[0-9]{2}-(?P<Row>[A-H])-(?P<Column>[0-9]{2})_(?P<rowtile>[0-9]{1,2})_(?P<coltile>[0-9]{1,2}).tif
11. Click Submit in Regular expression editor window.
12. Click Update button in lower portion to see information extracted for each of the images.
13. Click NamesandTypes directly below Metadata.
14. Change Assign a name to drop-down list to Image matching rules.
15. Enter Channel2- in blank field to right of Contain drop-down list.
16. Confirm DNA is entered in Name to assign these field.
17. Click Add another image button.
18. For second image set, enter Channel1- in blank field to right of Contain drop-down list.
19. Replace GFP in Name to assign these field with Cytoplasm.
20. Click Update button in lower portion.
21. Screen should resemble Figure T24.56 below for Regular expression editor window of Metadata module.
Notes:
•Follow these links for a tutorial on "Regular Expressions" and how to translate regular expressions.
•Setting up metadata and regular expressions only has to be done for one image in the set. For this example, it has been set up for Channel2.
•The regular expression output names: Well, Row, Column, rowtile and coltile may only be used with plate based or montage imaging experiments. These output names are reserved, and should not be used for anything aside from denoting the well and/or field positions.
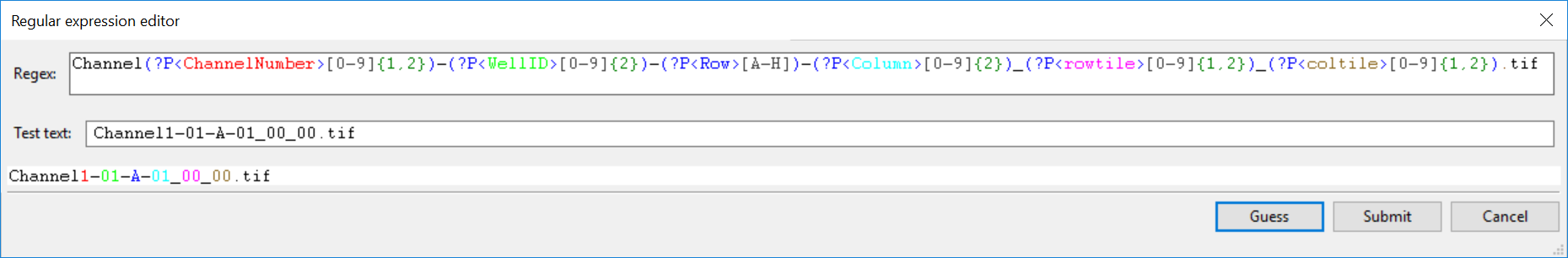
Figure T24.56 Setting up a Regular Expression in the LoadImages Module for a multiple field plate based experiment.
B. SaveImages Module
The image masks that were defined in the ConvertObjectsToImage modules must now be saved and related to the original images/data.
1.Select the first SaveImages module in the pipeline.
2.Set the Select the type of image to save drop-down list to Image.
3.Choose Cells for the Select the image to save drop-down list.
a.Note: when defining your own pipeline, select the appropriate image you defined in the ConvertObjectsToImage module.
4.Set the Select method for constructing file names drop-down list to Single name.
5.Enter CellLabel_ in the Enter single file name field.
6.Right-click after CellLabel_, choose Row, and enter an underscore "_"after it.
7.Right-click after Row_ and choose Column.
8.Right-click after Column_, choose rowtile, and enter an underscore "_"after it.
9.Right-click after rowtile_ and choose coltile.
10.Select the first SaveImages module in the pipeline.
11.Set the Select the type of image to save drop-down list to Image.
12.Choose Nuclei for the Select the image to save drop-down list.
13.Set the Select method for constructing file names drop-down list to Single name.
14.Enter NucleiLabel_ in the Enter single file name field.
15.Right-click after NucleiLabel_, choose Row, and enter an underscore "_"after it.
16.Right-click after Row_ and choose Column.
17.Right-click after Column_, choose rowtile, and enter an underscore "_"after it.
18.Right-click after rowtile_ and choose coltile.
Note: Row, Column, rowtile and coltile are values you defined as regular expressions for the load images module. Using regular expressions allows every output file to be assigned a unique file name based on the text from the input file name. This will prevent output file names from overwriting each other and allows FCS Express to identify the unique image mask associated with each image file.Perform steps 15-22 on both SaveImages modules set up for CellLabel and NucleiLabel.
19. Confirm tiff from the Saved file format drop-down list.
20. Set Image bit depth drop-down list to 16-bit integer.
21. Choose Default Output Folder from Output file location drop-down list.
22. Click Yes radio button in the Overwrite existing files without warning? box.
23. Set When to save as Every cycle from the drop-down list.
24. Click Yes radio button in Record the file and path information to the saved image? box.
The SaveImages module for CellLabel should now look like Figure T24.57
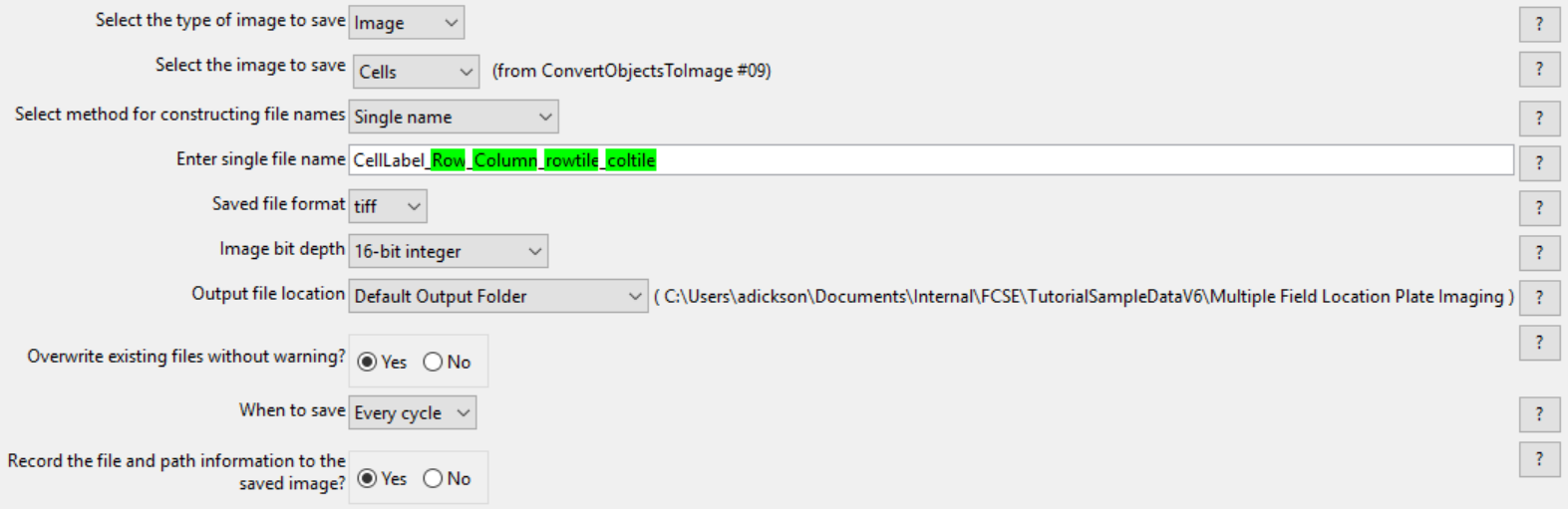
Figure T24.57 Defining the SaveImages Module
C. ExportToSpreadsheet Module
Now that all of the images and object image masks have been defined and saved for analysis, you must now ask CellProfiler to export the measurements you wish to view in FCS Express. For this example, we will export all measurements.
(Note: If you would like to only export certain parameters please see the Selecting Individual Parameters for CellProlifer Export section)
1.Select the ExportToSpreadsheet module.
2.Confirm the Select the column delimiter drop-down list is set to Comma (",").
3.Choose Default Output Folder from the Output file location drop-down list.
4.Click No radio button in the Add a prefix to file names? box.
5.Click No radio button in the Export all measurement types? box.
6.Choose Image from the first Data to export drop-down list.
7.Click No radio button in the Use the object name for the file name? box.
8.Replace DATA.csv with Image.cptoc in File name field.
9.Click Add another data set button.
10.Choose Nuclei from the second Data to export drop-down list.
11.Click No radio button in the Use the object name for the file name? box.
12.Replace DATA.csv with nuclei.cptoc in File name field.
13.Click Add another data set button.
14.Repeat steps 10-12 for "Cells" and set the file name as cells.cpout.
The ExportToSpreadsheet module options should look like Figure T24.58 when you are done.
Note 1: on file extensions: ".cptoc" stands for CellProfiler Table of Contents and ".cpout" stands for CellProfiler Output. The "Image.cptoc" file stores information about the location and number of images for all objects processed in the pipeline, while the separate "Nuclei.cpout" and "Cells.cpout" store the actual raw data associated with individual objects and analysis. There should be a separate ".cpout" file defined for each object mask defined in CellProfiler. Only one "Image.cptoc" file is needed.
Note 2:The name of your .cpout file must begin with the name of the object data you are exporting and may only be include the object name and regular expressions. For example: the file names nuclei.cpout and nuclei_<regular express>.cpout will result in a proper export while dataset1nuclei.cpout or <regularexpression>_nuclei.cpout will resulting in a non-working export.
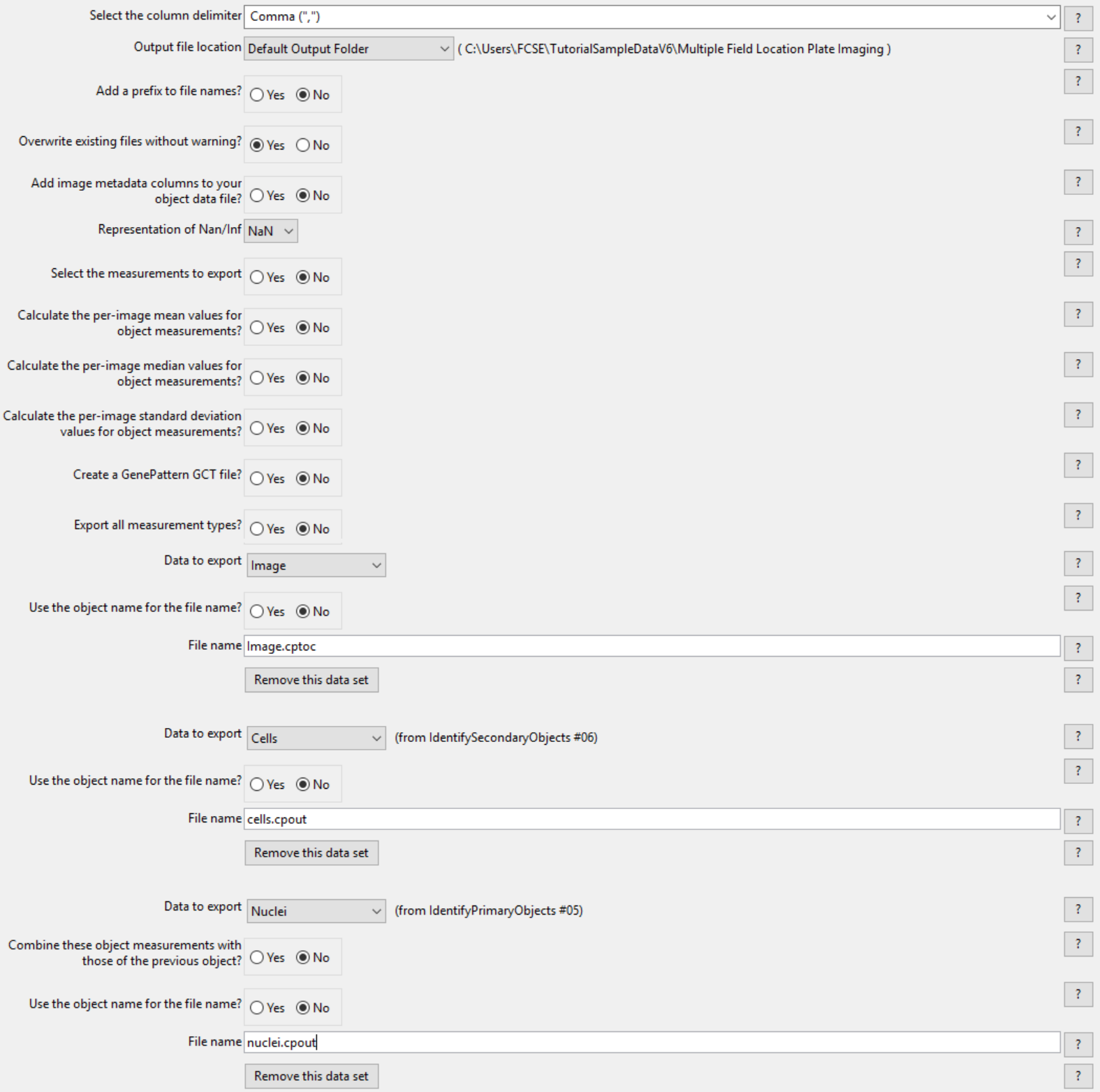
Figure T24.58 The ExportToSpreadsheet Module Set Up to Export image.cptoc, nuclei.cpout and cells.cpout.
15. Select Analyze images to run the pipeline. The folder where your images are stored will now contain the cells.cpout, nuclei.cpout, and Image.cptoc files. There will also be a CellLabel and NucleiLabel image associated with every original image from the data set.
In the next section, we will import and analyze the plate based multiple field location imaging data
