The Tools Tab
The Tools tab (Figure 3.30) contains four groups:
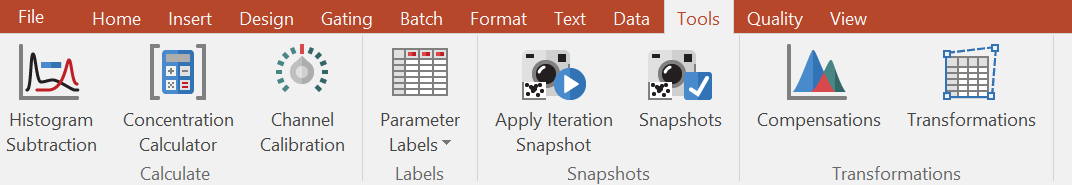
Figure 3.28 - Tools tab
•Calculate
oThe Histogram Subtraction command opens the Histogram Subtraction window where you can apply four mathematical methods of comparing sample and control histograms.
oThe Concentration Calculator command opens the Concentration Calculator window where you can calculate the concentration of events in a sample.
oThe Channel Calibration command opens the Channel Calibration window where you can change the axis fluorescence intensity scales from a linear or logarithmic scale to one indication either the absolute number of antigen molecules or the number of binding sites on the surface of a cell.
•Labels
oThe Parameter Labels opens a gallery containing Modify Labels, Load Labels, and Save Labels commands. These items allow the user to easily create, change, recall, and save alternate parameter labels.
•Snapshots
oThe Apply Iteration Snapshot command allows you to move gates between iterations and have the gates' new positions remembered while navigating using the Next and Previous commands.
oThe Snapshots command opens the Snapshot Navigator window where you can take custom snapshots of your analysis on data files and apply that analysis to other files. For example, a snapshot of a gate position may be taken, the gate position changed, and snapshot applied to go back to the original gate position.
•Transformations
oThe Compensations command opens the Compensations Navigator, which allows you to display the compensation information on the selected file, create new compensations, and load or save compensation information.
oThe Transformations command opens the Transformations Navigator, which allows you access K means (cluster analysis), Principal Component Analysis, Parameter Math (defines a single or sequence of math functions, save the functions, and apply the functions to data files), R integration to add new parameters or transformations, and tSNE.
